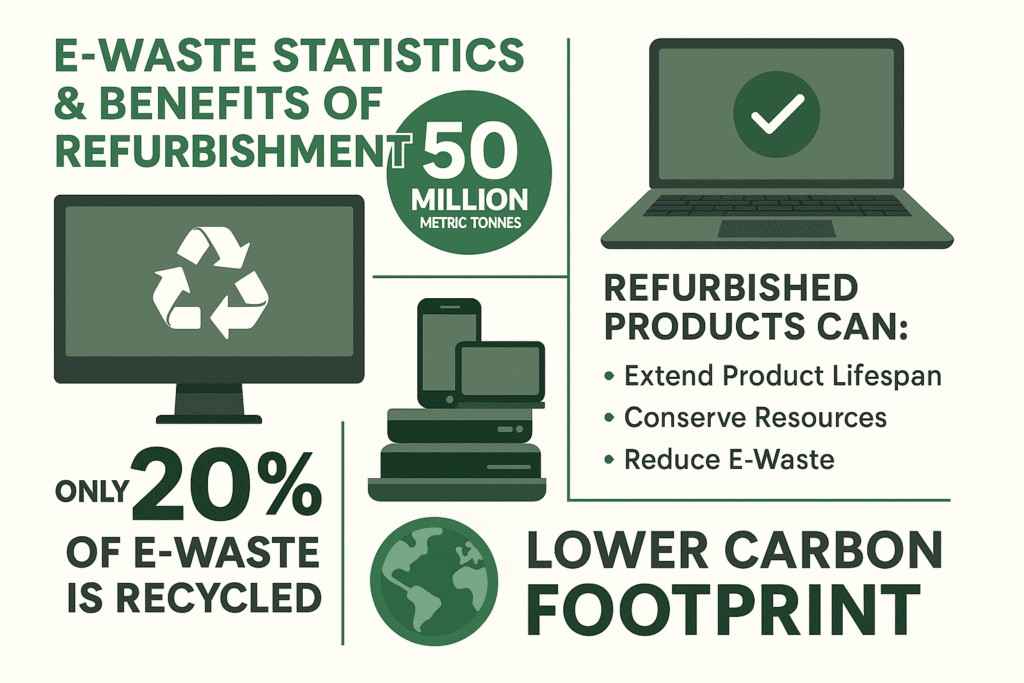
Every year, the world produces over 50 million tonnes of e-waste that’s old phones, laptops, kitchen appliances, and other electronics that end up discarded. Most of it never gets recycled. Instead, it piles up in landfills, releases toxic chemicals into the soil, or travels overseas where workers dismantle it in unsafe conditions.
The good news? We can slow this problem down, and one of the easiest ways is something many people don’t even think about: buying refurbished electronics and appliances. Not only does it keep devices out of landfills, but it also saves you money and helps cut down the demand for manufacturing brand-new tech.
This guide explains what E-Waste is, why it matters, and how refurbished goods can be a surprisingly powerful weapon in the fight against it.
What Is E-Waste?

E-Waste (short for electronic waste) refers to any discarded product with an electrical plug, battery, or circuit board. That includes:
- Smartphones and tablets
- Laptops and desktops
- TVs and monitors
- Printers, cameras, and audio gear
- Kitchen gadgets like blenders, air fryers, and coffee machines
- Large appliances like fridges and washing machines
People don’t throw away only “broken stuff.”” Many devices become e-waste long before they’ve truly reached the end of their usable life. People often replace them when a newer model comes out, when they could have repaired a small fault, or when marketing convinces them they need an upgrade.
The Growing Problem of E-Waste
The scale of e-waste is staggering — and growing fast. According to the Global E-Waste Monitor, electronic refuse is the fastest-growing solid waste stream in the world.
Here’s why it’s such a serious problem:

1. Toxic Components
Electronics contain hazardous substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, and flame retardants. When dumped, these can leach into soil and water, posing long-term health risks to humans and wildlife.
2. Resource Waste
Electronics are made using valuable metals like gold, silver, copper, and rare earth elements. Throwing them away means wasting resources that are expensive — and often environmentally destructive — to mine.
3. Carbon Footprint
Making new electronics requires huge amounts of energy. From mining raw materials to manufacturing and transporting products, the process contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Unsafe Recycling
In many cases, discarded electronics are shipped to developing countries, where they’re dismantled by hand without safety equipment, exposing workers to toxic chemicals.

How Refurbished Goods Can Help Reduce E-waste
Buying refurbished goods isn’t just a way to save money — it’s a direct way to fight e-waste. Here’s why:
1. Extending Product Lifespan Helps Reduce E-waste
When a phone, laptop, or appliance is refurbished, it gets repaired, cleaned, and tested so it works like new. This extends the product’s lifespan and delays its journey to the landfill.
2. Reducing Demand for New Manufacturing
Every time you buy refurbished instead of new, you’re reducing the demand for manufacturing brand-new electronics and all the mining, energy use, and carbon emissions that come with it.
3. Making Tech Accessible Helps Reduce E-Waste
Refurbished goods make high-quality devices more affordable, especially for students, families, and small businesses that might not have the budget for brand-new items.
4. Encouraging Repair Culture
When people see that products can be repaired and reused, it shifts consumer behaviour away from throwaway culture. That mindset change is key to tackling e-waste long-term.
Real-World Examples of E-Waste Reduction Through Refurbishment
Let’s look at a few real-world examples where refurbishment is making a difference:
- Apple Certified Refurbished: Apple takes back iPhones, MacBooks, and iPads, replaces faulty parts, installs new batteries, and resells them at a discount with a warranty.
- Amazon Renewed: Offers refurbished laptops, kitchen appliances, headphones, and more, all tested and certified by professional refurbishers.
- Back Market: A dedicated platform for refurbished electronics that partners with verified refurbishers and offers warranties to buyers.
All of these companies give electronics a second (or third) life — keeping them out of landfills and reducing the need to make new ones.
How You Can Make Eco-Friendly Tech Choices
Reducing e-waste doesn’t require you to be perfect just more intentional. Here’s how:
1. Buy Certified Refurbished
Look for products that come with a warranty and have been professionally tested. This ensures you get quality and reliability.
2. Trade-In or Sell Old Devices
Instead of throwing them away, trade them in for credit or sell them to refurbishers. Many retailers and manufacturers have trade in programs.
3. Repair Instead of Replace
If something breaks, see if it can be fixed. A new battery or screen can give a device years more life.
4. Donate Functional Electronics
If you’ve upgraded but your old device still works, donate it to schools, charities, or community organisations.
The Smart Refurbish Takeaway
E-waste isn’t an abstract problem it’s piling up in landfills and poisoning communities today. But by choosing refurbished goods, you’re directly reducing the waste stream, conserving valuable resources, and lowering your carbon footprint.
Plus, you’re getting high quality tech and appliances at a fraction of the price. It’s one of those rare win-win situations where what’s good for your wallet is also good for the planet.
If you’re ready to start making smarter, greener choices, check out Smart Refurbish’s guides to the best refurbished products on the market: